Lake Chad, once one of the largest freshwater lakes in Africa, has been facing significant ecological problems in recent decades. These issues have had far-reaching consequences for the surrounding communities and the fragile ecosystems that rely on the lake.
Endangered species
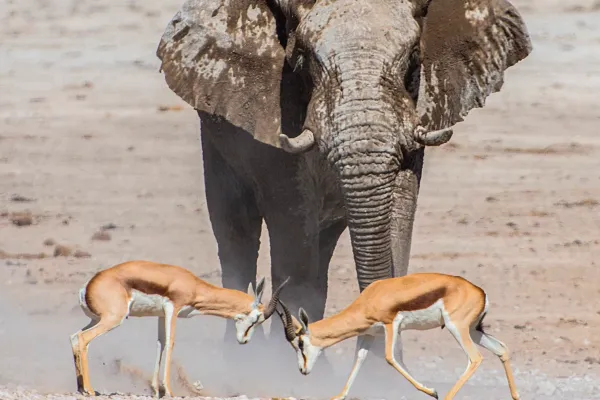
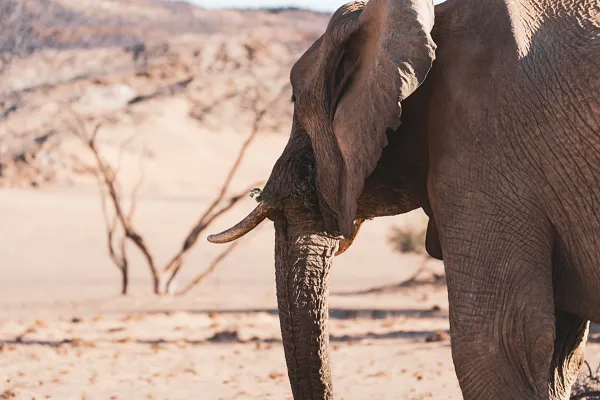
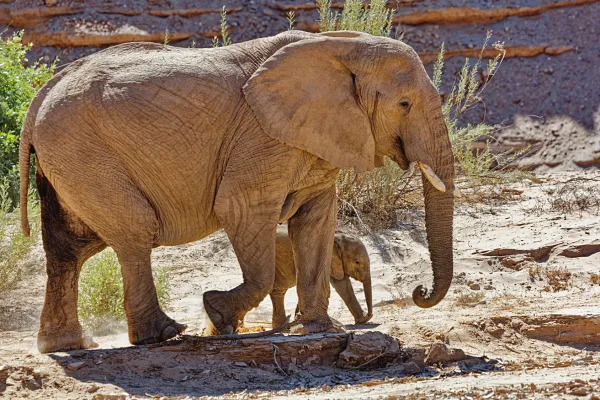
African elephant, oryx, addax, lion, African wild dog
Habitat
Wetland, marshes, savanna, Sahel, desert
Lake Chad, Nigeria, Niger, Chad, Cameroon
Size of area
243,400,000 ha
Carbon
? mT
Partner
ERuDeF, Local NGOs and CBOs
The Problem
Shrinking Water Resources
Lake Chad has experienced a drastic decline in water levels over the years, primarily due to reduced rainfall, climate change, and increased water demand for agriculture and human consumption. This shrinkage has resulted in a significant loss of water resources, impacting the entire ecosystem.
Loss of Biodiversity
The decline in water levels and changing environmental conditions have led to the loss of critical habitats within and around Lake Chad. Wetlands, marshes, and other important ecosystems have diminished, affecting the rich biodiversity that once thrived in the area. Several species of fish, birds, and aquatic plants have suffered due to the loss of their natural habitats.
Threat to Wildlife Migration
Lake Chad has traditionally served as a vital stopover and breeding ground for migratory birds and other wildlife. However, the diminishing water resources and changing landscape have disrupted these migration patterns, putting additional stress on already vulnerable species.
Addressing these ecological problems requires concerted efforts and collaboration among countries sharing the Lake Chad Basin.
What we do
Wetland restoration, reforestation, environmental education, protected areas, community-led conservation
Sustainable Water Management
Implementing sustainable water management practices is crucial to restore and maintain the water levels of Lake Chad. This involves improving water efficiency in agricultural practices, promoting water conservation measures, and regulating water usage to ensure the ecological needs of the lake and surrounding ecosystems are met.
Ecosystem Rehabilitation and Reforestation
Restoring critical habitats such as wetlands, marshes, and forests is essential for the recovery of biodiversity around Lake Chad. Our reforestation efforts will help stabilise soil erosion, provide shade and shelter for wildlife, and enhance the natural hydrological cycle. Additionally, restoring and protecting wetlands will support the regeneration of aquatic flora and fauna.
Capacity Development
Capacity development plays a crucial role in the restoration of Lake Chad by building the necessary skills, knowledge, and resources within individuals, communities, and institutions involved in the restoration efforts. Restoration projects for Lake Chad require specialized technical expertise in fields such as hydrology, ecology, water management, and reforestation.
By involving and engaging local communities, capacity development fosters a sense of ownership, collaboration, and responsibility for the long-term restoration and conservation of the lake’s ecosystems.
Sustainable Development Goals
Our project contributes to the following UN Sustainable Development Goals.